Rolling guides / profiled rail guides
Startseite » Linear technology » Profile Rail Guideways
What are rolling guides / profiled rail guides?
Rolling guides are generally all linear guides in which rolling elements are used. These include shaft and rail guides (profile rail guide, telescopic rail guide or cage rail guide). A rolling guide that is used particularly frequently in mechanical engineering is the profile rail guide. Its frequent use in practice results from the many advantages of this linear guide. High precision, load capacity, rigidity, operational reliability and service life are among the most important advantages of profile rail guides. They operate with pinpoint accuracy with the best running characteristics and meet the strict accuracy requirements of machine tools and other industrial precision applications.
Profile rail guides generally have one or more carriages located on a guide rail. The guide rail in turn has one or more hardened raceways. Between the carriage and the guideway are the characteristic rolling elements which roll on the hardened raceways and transmit the load. Care must always be taken to ensure good lubrication between the raceway and the rolling elements. This is because the lubricant used can have a strong influence on friction and wear and thus contributes to a long service life of rolling guides or profiled rail guides.
In general, rolling guides can be divided into guides with or without rolling element recirculation.
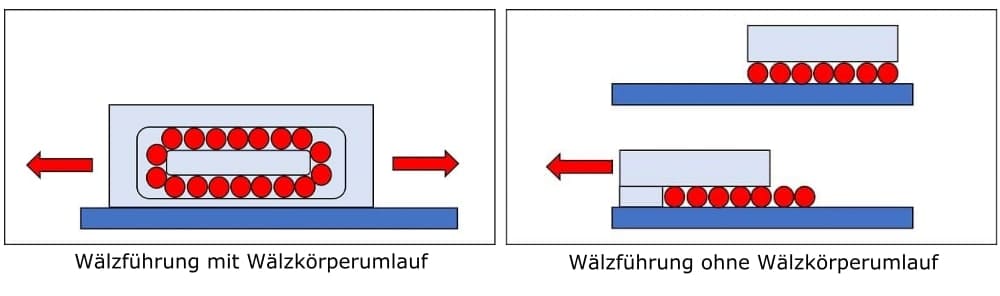
Design and function of rolling guides / profiled rail guides
With or without rolling element circulation
As already mentioned, a distinction is made between guideways with and without rolling element recirculation. Although the latter have the advantage of saving installation space, they can only cover a limited stroke distance due to a fixed number of rolling elements. In the case of guideways with recirculating rolling elements, the stroke is limited only by the rail length. The rolling elements themselves are always returned via the return stroke after load transmission. Typically, profiled rail guides have two, four or six rows of rolling elements. As the number of rows of rolling elements increases, the load-carrying capacity and rigidity of the profiled rail guide increases, since loads are carried by more rolling elements. However, friction also increases.
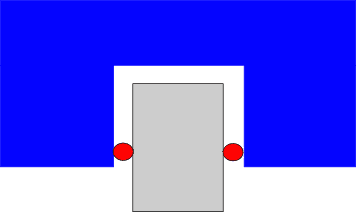
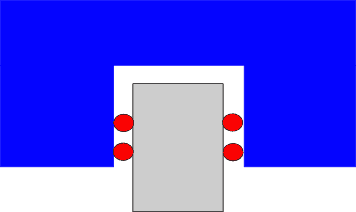
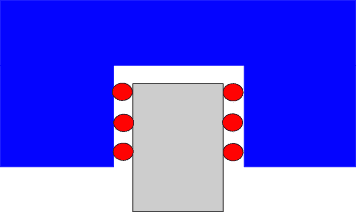
Ball or rollers as rolling elements
Both balls and rollers can be used as rolling elements. Due to different geometries, they also have different shapes of the contact surface, which in turn is reflected in different properties. Balls contact the contact surface only with a relatively small circular area, in the case of a linear guide an ellipse, since the raceway has the shape of a groove. Since the contact area is relatively small, the surface pressure is correspondingly high. An increase in the contact area and better load distribution is achieved by raceways with corresponding curvature. The curved shape of the raceway “nestles” around the ball surface, which increases load carrying capacity, rigidity and ultimately service life.
Compared to balls, the contact surfaces of rollers are not point-shaped but linear and significantly larger. This property allows rollers to transmit significantly greater forces. In addition, smaller sizes can be realized with rollers as rolling elements with the same load (compared to balls).
If balls are used as rolling elements, this is also referred to as profiled rail guides with ball bearings or linear recirculating ball bearing and guideway assemblies. However, if rollers are used as rolling elements, the linear guideways are also referred to as profiled rail guideways with roller bearings or linear recirculating roller bearing and guideway assemblies. Ball bearing profiled rail guides are particularly suitable for applications characterized by higher speeds and higher accelerations. Linear recirculating roller bearing and guideway assemblies are used when high loads and high rigidity are required.
Depending on the course of the force lines of action through the points of contact, one speaks of either an X or O arrangement of the raceways. Profile rail guides with an X arrangement have a shorter lever arm due to the smaller distance between the raceways. This facilitates misalignment in multi-axis systems (self-alignment). Profile rail guides with an O arrangement, on the other hand, have significantly higher rigidity and greater moment load capacity in the Mx direction and offer advantages in the case of lifting forces.
Buy rolling guides / profiled rail guides at PACH Systems
We offer a wide range of components for the realization of complete profile rail guides. These include recirculating ball and roller carriages, recirculating roller shoes and various guide rails. Please feel free to contact us and let us know your requirements.
PACH Systems offers you a large product range of different components for the realization of roller guides and profile rail guides. For this purpose, we cooperate with our long-standing suppliers. Please let us know your requirements via our contact form. We will be happy to submit you a non-binding offer or contact you to discuss the details.


